 |
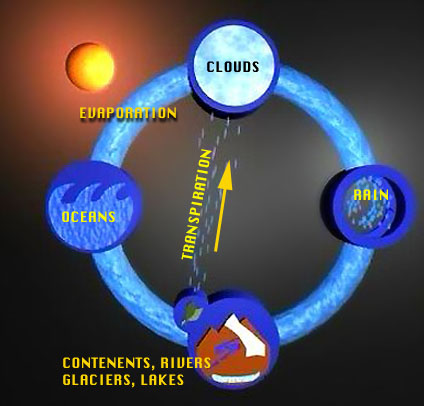
Hydrology Cycle Solar energy provides the heat necessary to evaporate water and create a gaseous phase. The water moves up into the earth's atmosphere and partially condenses to form a layer of clouds. After further condensation, the water (liquid phase) forms droplets or ice which fall back to the earth in the form of rain or snow. The water strikes the ground and coalesces to form streams, rivers, snow fields or glaciers. Gravity pulls the water from higher elevation to lower elevation providing it with the energy to erode solid surfaces. Eventually the water is stored in a reservoir (the ocean, a glacier, or lake) where it may continue its action of erosion by wave action or percolation (dissolution). |
Water is also captured by plants which my return it to the air via transpiration.
It may be part of a freeze and thaw cycle which can break rock by expanding and contracting in small fissures.
Finally the largest reservoir, the ocean, is responsible for most of the weather patterns on the earth which also produce wind and provide a means for further erosion.
| NEXT | TOC | PREV |